The Role of AI in Reducing Waste and Promoting Sustainability
Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force across various industries, and one of its most promising applications is in the realm of sustainability. From waste reduction and resource optimization to promoting circular economy practices, AI is playing a pivotal role in creating more sustainable systems. By harnessing the power of AI, we can not only minimize waste but also foster smarter, more efficient approaches to production, consumption, and disposal. Here’s a closer look at how AI is contributing to waste reduction and sustainability across different sectors.
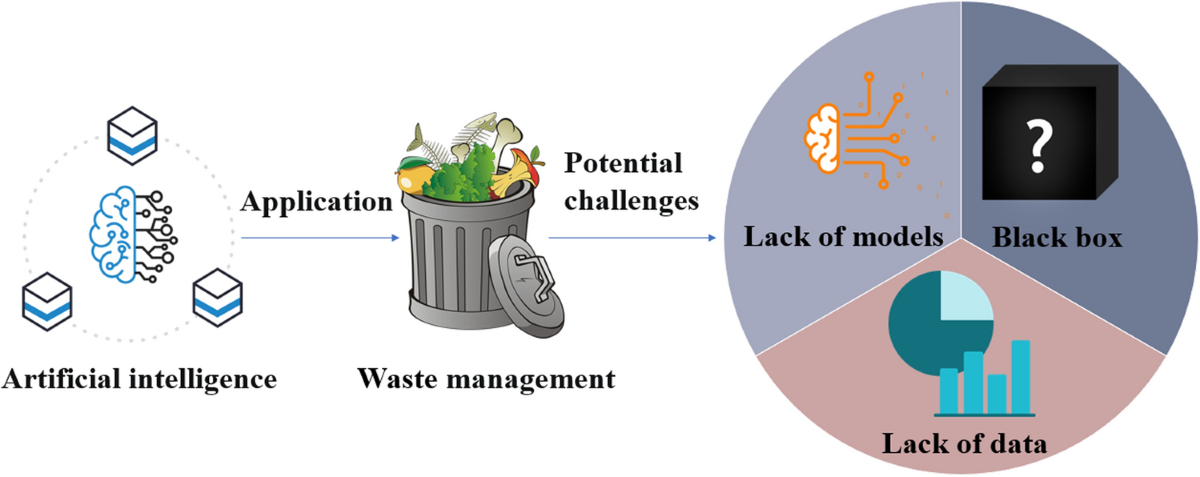
1. Smart Waste Management Systems
One of the most direct applications of AI in sustainability is in waste management. Traditional waste management systems often rely on manual sorting, inefficient transportation, and a one-size-fits-all approach to waste processing. AI is helping revolutionize this sector by enabling more efficient, data-driven, and automated processes.
AI-powered systems can use computer vision and machine learning algorithms to identify and sort waste materials more accurately than humans. These systems can automatically categorize recyclables like paper, plastic, and metal from non-recyclable waste, making recycling processes more effective. By optimizing waste sorting and reducing contamination, AI helps improve recycling rates and reduces the amount of waste that ends up in landfills or incinerators.
In addition, AI-driven systems can predict waste generation patterns and optimize collection routes for waste disposal trucks, reducing fuel consumption and carbon emissions. Smart waste bins equipped with sensors can track when they’re full and send notifications for collection, ensuring that resources are only used when needed.
2. Waste Reduction in Manufacturing and Supply Chains
AI is also playing a significant role in waste reduction within manufacturing and supply chains. Manufacturing processes often involve overproduction, excess materials, and inefficiencies that contribute to significant waste. AI can optimize these processes through predictive analytics, demand forecasting, and process automation.
For instance, AI algorithms can analyze historical data to predict future demand more accurately, helping manufacturers avoid overproduction and reduce excess inventory. This reduces the amount of unused products that would otherwise be discarded. In addition, AI-powered robots and automation systems can monitor production lines in real-time, identifying inefficiencies, and minimizing scrap materials.
AI can also optimize supply chains by identifying areas where resources are being wasted, such as unnecessary packaging or transport inefficiencies. By integrating AI into supply chain management, companies can make smarter decisions that reduce their environmental impact and promote sustainability throughout the entire production process.
3. Enhancing Energy Efficiency
AI plays a crucial role in improving energy efficiency, which is closely linked to waste reduction and sustainability. One of the primary ways AI contributes to energy savings is through predictive analytics and smart grid technology. AI-powered systems can monitor energy usage patterns in real time and make adjustments to optimize energy consumption, reducing waste and unnecessary energy expenditures.
For example, AI algorithms can analyze data from buildings or industrial facilities to detect inefficiencies in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. These systems can automatically adjust settings based on factors such as occupancy, weather forecasts, and time of day, ensuring that energy is not wasted. AI is also being used to optimize energy distribution in smart grids, ensuring that electricity is delivered efficiently to areas that need it the most, and reducing waste associated with energy transmission and storage.
In the renewable energy sector, AI is being used to predict energy generation from solar and wind power, improving the integration of these clean energy sources into the grid and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. By enhancing energy efficiency and supporting renewable energy adoption, AI contributes to a more sustainable and low-carbon future.
4. Promoting Circular Economy Practices
A circular economy is an economic system aimed at minimizing waste and maximizing the use of resources by reusing, repairing, and recycling products and materials. AI is playing a critical role in promoting circular economy practices by facilitating better resource management and enabling the development of more efficient recycling systems.
AI can help track and manage materials throughout their life cycle, ensuring that products are designed with their end-of-life in mind. For example, AI can be used to create digital product passports, which provide information about the materials used in a product, how it was made, and how it can be recycled. This transparency helps consumers and businesses make more sustainable purchasing and disposal decisions.
AI is also enabling innovations in product design by helping companies create products that are easier to disassemble, repair, or recycle. Machine learning algorithms can analyze large datasets to identify materials and designs that are more sustainable and easier to reuse, contributing to the overall circular economy model.
5. Reducing Food Waste
Food waste is one of the most pressing sustainability challenges, with significant environmental, economic, and social impacts. AI is helping reduce food waste by improving demand forecasting, optimizing food supply chains, and enhancing inventory management in the food industry.
AI-powered systems can predict consumer demand with greater accuracy, allowing food producers, retailers, and restaurants to adjust their supply and reduce overstocking. This minimizes the amount of unsold food that would otherwise go to waste. AI is also being used to monitor food quality, alerting businesses to potential spoilage or degradation, which can help prevent food from being discarded prematurely.
In the consumer space, AI-powered apps are helping individuals reduce food waste by suggesting recipes based on the ingredients they already have at home. These apps can help users plan meals more effectively, preventing them from buying unnecessary items and reducing food waste in the process.
6. Optimizing Water Usage
Water scarcity is another global sustainability challenge, and AI is helping optimize water usage across agriculture, industry, and urban environments. AI-driven systems can monitor and predict water usage patterns, allowing for more efficient distribution and conservation efforts.
In agriculture, AI-powered irrigation systems can adjust watering schedules based on real-time weather data, soil moisture levels, and plant needs, reducing water waste. AI can also be used to monitor water quality, detecting contaminants and optimizing treatment processes to ensure safe and sustainable water usage.
For urban areas, AI can improve water management by identifying leaks in pipes, optimizing water distribution, and ensuring that water resources are allocated efficiently. By reducing water waste and improving conservation efforts, AI helps address water scarcity and promotes more sustainable water management practices.
7. AI in Environmental Monitoring and Protection
AI is also helping monitor and protect the environment by providing real-time data and insights into environmental conditions. AI algorithms can analyze data from sensors and satellites to track pollution levels, monitor deforestation, and assess the health of ecosystems. This data-driven approach enables more effective environmental management and policy decision-making.
For example, AI-powered systems can detect illegal deforestation activities or track the movement of endangered species in real-time, helping conservationists take swift action. In urban environments, AI can be used to monitor air quality, noise pollution, and waste management, enabling cities to take proactive steps to improve environmental conditions and reduce waste.
Conclusion
AI is playing an increasingly crucial role in promoting sustainability by reducing waste, improving efficiency, and supporting the transition to a circular economy. From optimizing waste management systems and supply chains to reducing food and water waste, AI is enabling smarter, more sustainable practices across a variety of sectors. As AI technologies continue to evolve, their potential to address the world’s most pressing environmental challenges grows, offering new opportunities for individuals, businesses, and governments to work together toward a more sustainable future.
By leveraging the power of AI to reduce waste and maximize resource efficiency, we can build a more sustainable world that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. The integration of AI in sustainability efforts represents a vital step in ensuring that our planet remains habitable, healthy, and resilient for years to come.

Your passion is infectious. It’s hard not to get pumped about the things you discuss.
I’m astonished at your capacity to make even the most everyday topics engaging. Kudos to you!
9xg25o