5G Technology: How It Will Impact the Future of Connectivity
5G technology is set to revolutionize the way we connect, communicate, and interact with the world around us. As the fifth generation of mobile network technology, 5G promises to deliver faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity than its predecessors, enabling a new era of connectivity that will impact everything from daily consumer experiences to large-scale industrial applications. With the rollout of 5G networks gaining momentum worldwide, we’re beginning to see just how transformative this technology will be across industries and society as a whole. But what exactly is 5G, and why is it so important for the future?
What is 5G Technology?
5G is the next evolution of cellular networks, following 4G (LTE) technology. It is designed to provide significantly faster data speeds, improved reliability, and lower latency, which is the delay between sending and receiving data. 5G uses a combination of new technologies, such as millimeter-wave frequencies, massive MIMO (multiple-input multiple-output) antennas, and beamforming, to enhance network performance. These innovations allow for a more efficient use of the available spectrum, enabling faster data transmission, lower congestion, and more simultaneous connections than ever before.
While 4G networks have been adequate for today’s internet usage, including streaming videos and browsing the web, 5G is designed to meet the demands of a future where devices, systems, and people are even more connected, automated, and reliant on real-time data.
Key Impacts of 5G Technology on Connectivity
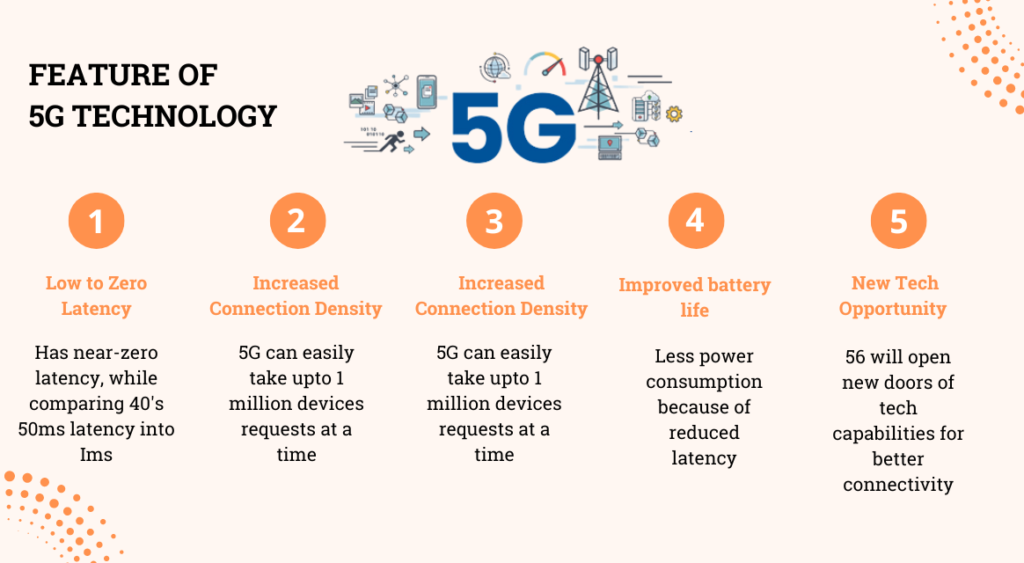
- Ultra-Fast Speeds and Greater Bandwidth One of the most anticipated benefits of 5G is its lightning-fast speeds. With 5G, download speeds can reach up to 10 gigabits per second (Gbps)—up to 100 times faster than 4G. This means that large files, such as high-definition videos, games, and software, can be downloaded in a fraction of the time. For consumers, this translates into virtually lag-free experiences when streaming ultra-high-definition content, gaming, or using augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) applications.
The increased bandwidth offered by 5G will also support more devices on the network, reducing congestion and ensuring that more people and IoT devices can stay connected simultaneously without a dip in performance.
- Low Latency for Real-Time Connectivity Latency refers to the time it takes for data to travel from one point to another. 5G dramatically reduces latency, potentially bringing it down to just 1 millisecond (ms), compared to the 30-50 ms latency typically seen with 4G. This near-instantaneous data transmission will be a game changer for industries that rely on real-time communication and decision-making.
For example, self-driving cars will depend on low-latency connections to process vast amounts of data from sensors and cameras in real-time, enabling them to make decisions quickly enough to avoid accidents. Similarly, remote surgery could become a reality, where surgeons control robotic instruments in real-time over a 5G network, regardless of distance.
- Enhanced Connectivity for the Internet of Things (IoT) The IoT, which refers to the network of interconnected devices that communicate and share data with each other, is growing exponentially. From smart homes to industrial machines, 5G will provide the infrastructure needed to handle the billions of devices expected to be connected in the coming years.
With its ability to support a massive number of devices simultaneously without sacrificing performance, 5G will enable a more seamless and reliable IoT ecosystem. Smart cities, for example, will benefit from 5G networks to optimize everything from traffic management to waste collection and energy usage, improving overall efficiency and sustainability.
- Empowering Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) applications require significant data processing to provide immersive, real-time experiences. 5G’s high bandwidth and low latency will allow AR and VR technologies to flourish in new ways, transforming industries like gaming, entertainment, education, healthcare, and retail.
Imagine a world where you can step into a virtual meeting room with colleagues from around the world, experiencing lifelike avatars and interactive objects in real-time, or shopping in an immersive virtual store. With 5G, these types of experiences will become more common, as the technology will support smooth, lag-free interactions that are essential for both personal and professional use.
- Advancements in Smart Cities and Infrastructure The implementation of 5G will play a key role in the development of smart cities, which rely on advanced connectivity to improve the quality of urban life. From autonomous public transportation to real-time traffic monitoring and environmental sensing, 5G networks will provide the speed and reliability needed to support smart infrastructure.
For example, traffic lights connected to 5G networks could adjust dynamically to real-time traffic conditions, reducing congestion and improving safety. Similarly, energy grids can be optimized in real-time for better efficiency, reducing waste and ensuring a more sustainable future.
- Revolutionizing Healthcare 5G will also have a profound impact on healthcare, enabling innovations that improve patient care, enhance efficiency, and reduce costs. With its ultra-low latency and high bandwidth, 5G will enable telemedicine to reach new heights, allowing doctors to remotely monitor patients, conduct virtual consultations, and perform complex medical procedures via robotic surgery with real-time data transmission.
Additionally, wearable health devices can transmit data to healthcare providers continuously, allowing for better disease management and early detection. 5G networks will also facilitate the development of medical research tools that process large amounts of health data quickly, helping researchers discover new treatments and solutions faster.
- Transforming Manufacturing and Industry 4.0 5G will enable the next wave of industrial automation by powering Industry 4.0—a revolution in manufacturing that involves the use of IoT, artificial intelligence, robotics, and big data. In manufacturing environments, 5G will allow machines, sensors, and robots to communicate with each other and with humans seamlessly in real-time. This can lead to more efficient production lines, improved quality control, predictive maintenance, and safer working environments.
With 5G’s ability to provide low-latency, high-bandwidth connections, factories will be able to adopt fully automated systems that can respond instantly to changes in demand, defects, or unexpected issues, optimizing production processes like never before.
Challenges and Considerations for 5G
While 5G promises to bring about extraordinary improvements, there are still several challenges to overcome. The rollout of 5G networks requires significant infrastructure investment, including the installation of new cell towers and small cells to ensure proper coverage. Additionally, the higher frequencies used by 5G (especially in mmWave spectrum) have limited range and can be easily obstructed by physical barriers, requiring a denser network of antennas.
Another concern involves the potential health implications of increased exposure to electromagnetic radiation, although current scientific research has not found any conclusive evidence that 5G networks pose significant health risks.
Conclusion
5G technology is poised to dramatically reshape the future of connectivity, with far-reaching implications for industries, economies, and everyday life. Its ultra-fast speeds, low latency, and ability to connect billions of devices will unlock new possibilities in everything from autonomous vehicles and healthcare to entertainment and smart cities. While there are challenges in deploying and maintaining 5G networks, the transformative potential of this technology is undeniable, and as it becomes more widely available, we can expect the digital landscape to evolve in ways we are just beginning to imagine. The future of connectivity is 5G—and it’s coming fast.



Great post, I truly had a great time reading it. Your way of writing is very captivating and the ideas are very relevant. Thank you for sharing!
Your blog has rapidly become my favorite source for inspiration. I crave for more!
Sprunki Game truly elevates the Incredibox experience with its rich sounds and visual flair. It’s a fresh twist on musical creativity that feels both nostalgic and innovative. Check it out at Sprunki Game!