The Impact of 5G on IoT and Smart Cities
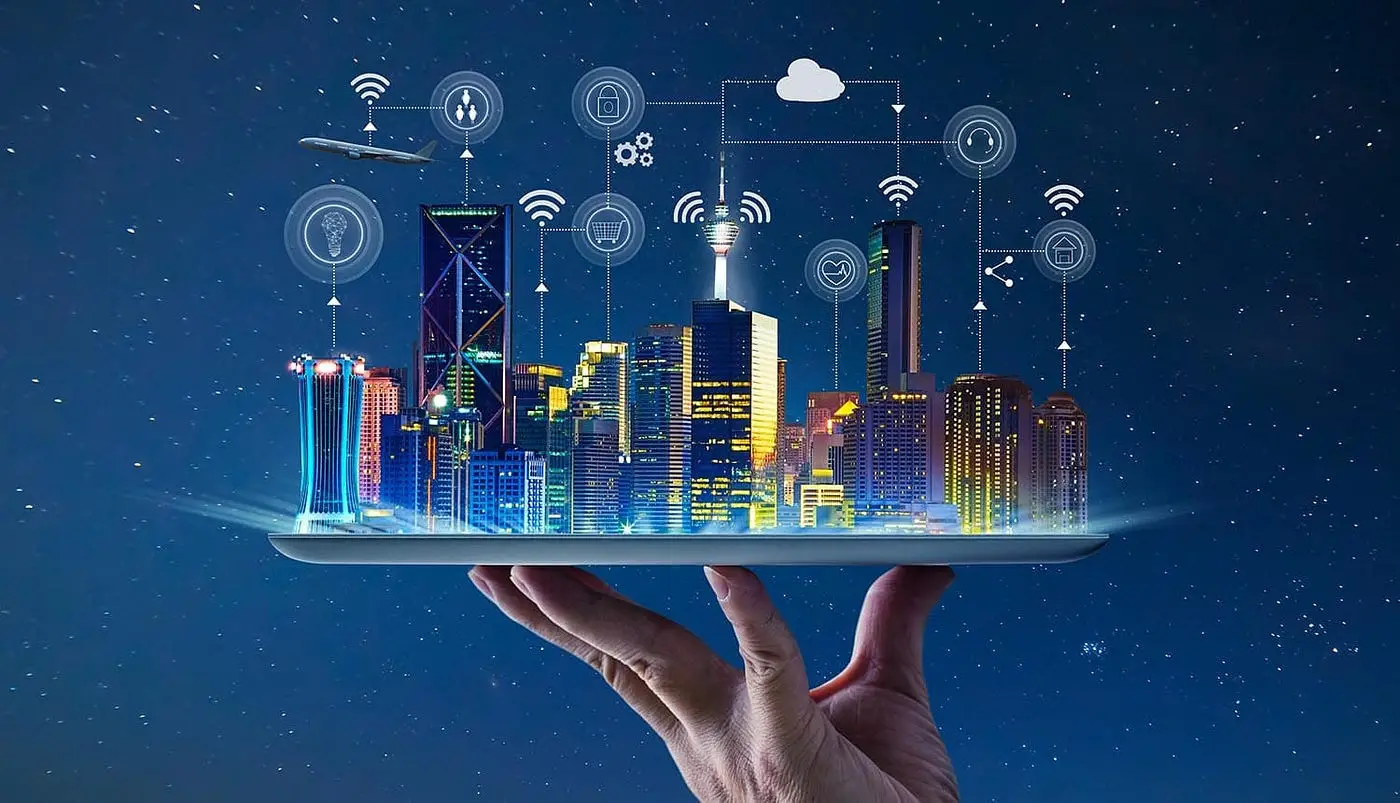
What is a smart city?
The European Commission defines a smart city as “a place where traditional networks and services are made more efficient with the use of digital and telecommunication technologies for the benefit of its inhabitants and business”. Diffusion and availability of new technologies are required to transform a city into a smart city, contributing to reach high level of urban sustainable development and improved quality of life for its citizens.
A smart cities use Internet of Things (IoT) to collect real time data to better understand how demand patterns are changing, and respond with faster and lower-cost solutions. Broadly speaking, digital city ecosystems are designed to run on ICT frameworks that connect several dedicated networks of mobile devices, sensors, connected cars, home appliances, communication gateways and data centers.
Smart cities, one of the key application areas of 5G and IoT technologies, have at their core the goal of improving quality of life, creating collaborative solutions, and addressing resource constraints. Examples of some of the many services integrated into the network of a typical smart city are related to smart health, smart transportation, smart buildings, smart hotels, smart industry, smart universities, etc. The new era of wireless mobile telecommunication technology and the IoT ecosystem is driving the opportunities for smart cities to not only solve existing problems but also create new services and functionalities that are out of the box and invisible to the end user. The main objective of this paper is to explore the role of 5G and IoT in smart cities. The market environment, key business developments, and trends related to the key smart cities’ enablers, IoT and 5G, are presented. An in-depth literature review followed by a discussion is substantiated with synthesized research findings on the current development, 5G coverage, use and deployment of IoT in smart cities, and forecasting the evolution of its application in smart cities.
By 2025 the IoT trends suggest the number of connected devices worldwide will rise to 75 billion. The increasing number of objects that interconnect generates an unprecedented volume of data that the city can analyze locally in order to make more informed decisions about what changes or new projects will most benefit residents. The term “Massive IoT” is an apt description of the enormous number of IoT sensors and devices that will be communicating with each other.
Conclusion:
The rollout of 5G technology is set to have a profound impact on the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart cities, revolutionizing the way devices connect, communicate, and operate. With 5G’s faster speeds, lower latency, and higher capacity, it enables IoT devices to transmit data at unprecedented rates, making real-time communication and automation more efficient. For smart cities, 5G paves the way for the development of advanced infrastructure, such as smart traffic systems, autonomous vehicles, and connected public services. This allows for better traffic management, reduced congestion, and optimized energy use. Additionally, 5G enhances the reliability of devices, supporting a vast number of IoT connections without network overload. It also improves remote monitoring and management capabilities, benefiting industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and urban planning. The increased bandwidth and lower latency of 5G can enable more accurate environmental monitoring, smarter resource allocation, and faster emergency response times in cities. Ultimately, 5G will not only advance the capabilities of IoT devices but also accelerate the evolution of smart cities into more connected, efficient, and sustainable ecosystems.



ocvmi OZFliXwI XdQJOuBN UYiTAd gWzyLLZ ddxOWBq lPiQfmYC
Loved the breakdown! Platforms like Jili77 are raising the bar with AI-driven insights that give players a smarter edge in virtual gaming.
Москва. МСК психолог Измайлово Психолог в Москве.
Задайте интересующие вас вопросы или запишитесь на сеанс к психологу.
Сколько встреч нужно?
Мы обязательно поможем преодолеть эмоциональный кризис, избавиться от тревожности и апатии, справиться со стрессом и депрессией, связанными с неуверенностью и многим другим.
Понимание своего Дизайна Человека может помочь в выборе жизненного пути, который лучше соответствует вашему характеру и предназначению. 53 42
Каждый Профиль состоит из двух Линий: Сознательной и Подсознательной.
12 профилей в Дизайне человека. Исследователь. Отшельник. Мученик. Оппортунист. Еретик. Ролевая модель.
Дизайн Человека позволяет учитывать индивидуальные особенность каждого человека и учит познавать свою истинную природу.
Тип – это основа, но ваша уникальность проявляется через Профиль, Центры, Каналы и Ворота.
Анализ своего Дизайна Человека может помочь в понимании причин, по которым вы испытываете определенные трудности, разочарования, и как можно их преодолеть. Манифестор 1 3
Анализ своего Дизайна Человека может помочь в понимании причин, по которым вы испытываете определенные трудности, разочарования, и как можно их преодолеть.
В целом, Дизайн человека может быть полезным инструментом для самопознания, саморазвития, и улучшения качества жизни. Он помогает понять себя и окружающий мир, и найти свой путь, который приносит счастье и удовлетворение.
Дизайн человека может помочь вам лучше понимать людей вокруг вас, их энергетический тип, и как лучше взаимодействовать с ними.
Дизайн Человека (human design) – это система знаний об энергетической механике людей и космологическом устройстве мира.
Дизайн Человека (human design) – это система знаний об энергетической механике людей и космологическом устройстве мира. 44 ворота дизайн человека
Каждый Профиль состоит из двух Линий: Сознательной и Подсознательной.
Анализ своего Дизайна Человека может помочь в понимании причин, по которым вы испытываете определенные трудности, разочарования, и как можно их преодолеть.
Дизайн человека помогает понять, какой тип энергии вы излучаете, как вы принимаете решения, и как лучше использовать свою энергию, чтобы не выгорать, а чувствовать себя более удовлетворённым
В целом, Дизайн человека может быть полезным инструментом для самопознания, саморазвития, и улучшения качества жизни. Он помогает понять себя и окружающий мир, и найти свой путь, который приносит счастье и удовлетворение.
Mobile gaming is evolving so fast! Seeing platforms like PH Login really focus on the experience – intuitive interfaces & fast loading are key. Optimizing for those micro-interactions is smart, making gameplay seamless!
Профили в Дизайне человека · 1 линия — Исследователь · 2 линия — Отшельник · 3 линия — Мученик · 4 линия — Опортунист · 5 линия — Еретик · 6 линия — Ролевая модель. Рассчитать дизайн человека совместимость
Дизайн человека помогает понять, какой тип энергии вы излучаете, как вы принимаете решения, и как лучше использовать свою энергию, чтобы не выгорать, а чувствовать себя более удовлетворённым
Дизайн Человека (human design) – это система знаний об энергетической механике людей и космологическом устройстве мира.
Анализ своего Дизайна Человека может помочь в понимании причин, по которым вы испытываете определенные трудности, разочарования, и как можно их преодолеть.
Дизайн человека помогает понять, какой тип энергии вы излучаете, как вы принимаете решения, и как лучше использовать свою энергию, чтобы не выгорать, а чувствовать себя более удовлетворённым Ворота 33 дизайн человека
Профили в Дизайне человека · 1 линия — Исследователь · 2 линия — Отшельник · 3 линия — Мученик · 4 линия — Опортунист · 5 линия — Еретик · 6 линия — Ролевая модель.
Профиль в Дизайне Человека — это уникальная комбинация двух линий, которые формируют ваш характер и способы взаимодействия с миром.
Понимание своего Дизайна Человека может помочь в выборе жизненного пути, который лучше соответствует вашему характеру и предназначению.
12 профилей в Дизайне человека. Исследователь. Отшельник. Мученик. Оппортунист. Еретик. Ролевая модель.
Дизайн человека помогает понять, какой тип энергии вы излучаете, как вы принимаете решения, и как лучше использовать свою энергию, чтобы не выгорать, а чувствовать себя более удовлетворённым
В целом, Дизайн человека может быть полезным инструментом для самопознания, саморазвития, и улучшения качества жизни. Он помогает понять себя и окружающий мир, и найти свой путь, который приносит счастье и удовлетворение.
Для каждого человека естественного искать выгоду для себя. Так происходит и с Дизайном Человека. Расчет соляра
Для каждого человека естественного искать выгоду для себя. Так происходит и с Дизайном Человека.
Дизайн человека делит людей на четыре категории, помогает узнать себя и показывает путь к счастливой жизни.
Тип – это основа, но ваша уникальность проявляется через Профиль, Центры, Каналы и Ворота.
Дизайн человека – это система, которая предлагает анализ личности на основе информации о дате, времени и месте рождения.
12 профилей в Дизайне человека. Исследователь. Отшельник. Мученик. Оппортунист. Еретик. Ролевая модель.
Дизайн Человека (human design) – это система знаний об энергетической механике людей и космологическом устройстве мира.
Для каждого человека естественного искать выгоду для себя. Так происходит и с Дизайном Человека. Манифестор 4 6
Дизайн человека делит людей на четыре категории, помогает узнать себя и показывает путь к счастливой жизни.
Профиль в Дизайне Человека — это уникальная комбинация двух линий, которые формируют ваш характер и способы взаимодействия с миром.
Дизайн Человека позволяет учитывать индивидуальные особенность каждого человека и учит познавать свою истинную природу.
Понимание своего Дизайна Человека может помочь в выборе жизненного пути, который лучше соответствует вашему характеру и предназначению.
Тип – это основа, но ваша уникальность проявляется через Профиль, Центры, Каналы и Ворота.
В целом, Дизайн человека может быть полезным инструментом для самопознания, саморазвития, и улучшения качества жизни. Он помогает понять себя и окружающий мир, и найти свой путь, который приносит счастье и удовлетворение.
Множество стратегий и подходов, которые могут помочь нам справиться с жизненными вызовами. Консультация
Человек может ставить новые цели, расширить свой кругозор, заниматься спортом или творчеством.
Жизненные трудности – это любые ситуации, которые могут нарушить привычный жизненный уклад и потребовать значительных усилий для их преодоления.
Любой человек в своей жизни сталкивается с чередой испытаний.
DXwYF hilCC GVKsyB nKrafwJ GMYVmY ZypuxYb xDK
Перестроим же свое сознание и тогда вслед за мыслями, изменится мир вокруг нас. (Наталья Правдина) https://mans-naletchik.citaty-tsitaty.ru
В 1980-х и 1990-х годах сеть стала коммерческой. Иерархии в науке и математике. Ребенок спрашивает, как запомнить слова, чтобы подготовиться к тесту. [Пирамида уровней Дилтса-Короткова –
Dice games offer a thrilling mix of luck and strategy, and platforms like Jili Online bring that excitement with slots and live games. The variety and user-friendly interface really stand out.
Миссия определяется в терминах «сервиса». [Пирамида Дилтса –
Сайт с психологами. Получить КОНСУЛЬТАЦИЮ и ПОДДЕРЖКУ профессиональных психологов. Мне нужен хороший психолог.
Психотерапевт Оренбург. Психотерапевты Самара. 584 оценок
На прием Клинцы. В17 психология. 903 оценок
Б17 психологи. Психотерапевт Пенза. 471 оценок
Психотерапевт Челны. Кпт курган. 490 оценок
Психотерапевт Белгород. Б17 психологи. 944 оценок
В17 психология. batmanapollo.ru 519 оценок
В17 психология. batmanapollo.ru 185 оценок
На прием Клинцы. Психолог 767 915 оценок
В17 психология. professorkorotkov.ru 802 оценок
Кпт курган. chat-s-psikhologom-v-telegramme.ru 747 оценок
Психотерапевт Оренбург. chat-s-psikhologom-v-telegramme.ru 203 оценок
Кпт курган. Психиатр онлайн 753 оценок
Кпт курган. Психиатр онлайн 828 оценок
Сервис по подбору психолога Психолог онлайн 456 оценок
Психотерапевт Киров. Психолог онлайн 272 оценок
В17 психология. Психотерапевт онлайн 868 оценок
Психотерапевт Белгород. Психиатр онлайн 795 оценок
Психотерапевты Самара. Психиатр онлайн 782 оценок
Как компактно сложить вещи в чемодан Как компактно собрать чемодан 116 благодарностей
Психолог оценили 9024 раз
Дизайн человека 31 27
23 Ворота Дизайн человека
4 Ворота Дизайн человека
2 Ворота Дизайн человека
40 Ворота Дизайн человека
17 Ворота Дизайн человека
39 Ворота Дизайн человека
11 Ворота Дизайн человека
6 Ворота Дизайн человека
30 Ворота Дизайн человека
20 Ворота Дизайн человека
35 Ворота Дизайн человека
Дизайн человека 32 25
64 Ворота Дизайн человека
7 Ворота Дизайн человека
8 Ворота Дизайн человека
56 Ворота Дизайн человека
24 Ворота Дизайн человека
14 Ворота Дизайн человека
22 Ворота Дизайн человека
31 Ворота Дизайн человека
44 Ворота Дизайн человека
30 Ворота Дизайн человека
56 Ворота Дизайн человека
Дизайн человека 35 63
28 Ворота Дизайн человека
22 Ворота Дизайн человека
53 Ворота Дизайн человека
53 Ворота Дизайн человека
53 Ворота Дизайн человека
31 Ворота Дизайн человека
2 Ворота Дизайн человека
57 Ворота Дизайн человека
14 Ворота Дизайн человека
11 Ворота Дизайн человека
49 Ворота Дизайн человека
Психолог 49 4
Психолог 55 9
Психолог 53 63
Психолог 29 44
https://t.me/s/Official_1win_kanal/1109
https://t.me/s/Webs_1WIN
хумдес ком хьюман дизайн кто я human design online
рассчитать профиль по дизайну человека рассчитать дизайн человека расшифровка карты дизайна человека
рев карта дизайна человека карта хьюман дизайн дизайн человека типы личности рассчитать
https://t.me/Official_blog_1win
https://t.me/s/onewin_kanal/10380
ntlgfw6498
Психолог
https://t.me/s/Official_1xbet_1xbet/1332
https://t.me/s/Official_1xbet_1xbet/508
Психолог
Психолог
Психолог
Крылатые выражения 5 класс. Люди потребители цитаты. Цитаты о мыслях. Цитата на день. Самые красивые слова. Цитаты ученых.
Цитаты про горе. Начни с себя цитата. Все будет хорошо цитата. Слова мудрецов о жизни. Цитаты знаменитых людей. Мотивирующая цитата. Мудрые стихи про жизнь. Позитивный человек цитаты.
Привет всем!
Долго думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
энтузиастов ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Линкбилдинг линкбилдинг сайта ускоряет продвижение. Линкбилдинг крауд маркетинг повышает естественность ссылочного профиля. Линкбилдинг форум помогает находить новые источники ссылок. Линкбилдинг с чего начать узнают новички. Линкбилдинг отзывы подтверждают эффективность методов.
seo title seo description, ашманов книга seo, Ускоренный рост ссылочного профиля
Повышение авторитетности домена, seo оптимизация картинок, seo продвижение сайта анализ
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Добрый день!
Долго не мог уяснить как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить DR и узнал от крутых seo,
крутых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Прогон ссылок через Xrumer ускоряет увеличение DR и Ahrefs. Массовые рассылки на форумах помогают создавать качественные внешние ссылки. Автоматизация линкбилдинга с помощью Xrumer даёт быстрые результаты. Программы для линкбилдинга позволяют охватить множество площадок. Начните использовать Xrumer для эффективного роста сайта.
seo links building, seo генерируемое описание, SEO рассылки форумов
Автоматическое размещение ссылок, semantic seo, продвижение сайта на cms
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
youtube 6619
youtube 6225
youtube 6174
youtube 7820
youtube 8624
youtube 1536
6333
4750
1042
7589
Visit euo
zqd08r
Link tet